March of the robo-researchers 🤖✨
Does the new wave of AI-assisted research tools spell the end for human researchers? (No.)
Welcome to The Navigator 🧭 - a newsletter about people, technology and design for business leaders who want to make meaningful change. I’m Sarah Ronald, and I write this newsletter with the Nile team. If this email was forwarded to you, you can subscribe here to receive it straight to your inbox.
Hello! 👋
For this month’s feature, I’m handing over to our Head of Design Research, Dr Alexa Haynes. She investigates whether the new breed of AI-powered research tools delivers the goods – and explores how researchers can use AI mindfully and responsibly.
We’ve also got our latest round-up of goings-on at Nile, including our Changemakers’ Breakfast, the FCA’s Financial Inclusion TechSprint and more.
Wishing you all the best as you navigate your week.
– Sarah
I thought AI was coming for my job… but now I know I’m safe. For now.
Our Head of Design Research, Dr Alexa Haynes, on whether AI-assisted research tools are a help or a hindrance
Back in 2023, with headlines flying around claiming AI was about to replace 60% of jobs, I was worried. And with good reason – near the top of the list, in black and white, was ‘Researcher’.
I was very happy in my role. Were all my years of hard work about to be undone by some code that isn’t much more than autocomplete on steroids? I had to find out.
Over the last few months, I’ve spent time investigating and testing the features of the new breed of research tools that are enhanced with AI.
They all claim to make analysis faster, better and more accurate – and they all claim they’ll make my job easier. But do the claims stand up?
I came at the task from a place of anxiety, and to some extent scepticism. I had all sorts of questions whirling around my head:
What tools are out there?
How can they best be employed?
How much time will they save me?
Can they write guides?
Will they do all my analysis for me?
…and, most importantly, will I be replaced?
What I found surprised me. There’s actually a lot of variation in how AI is being applied within research tools and the resulting quality of their output. At best, they did speed up some processes, and I can see how they’d fit into the researcher’s toolkit. At worst, though, some of the tools provided misleading summaries and outputs – which is not just unacceptable, but could result in serious reputational impact.
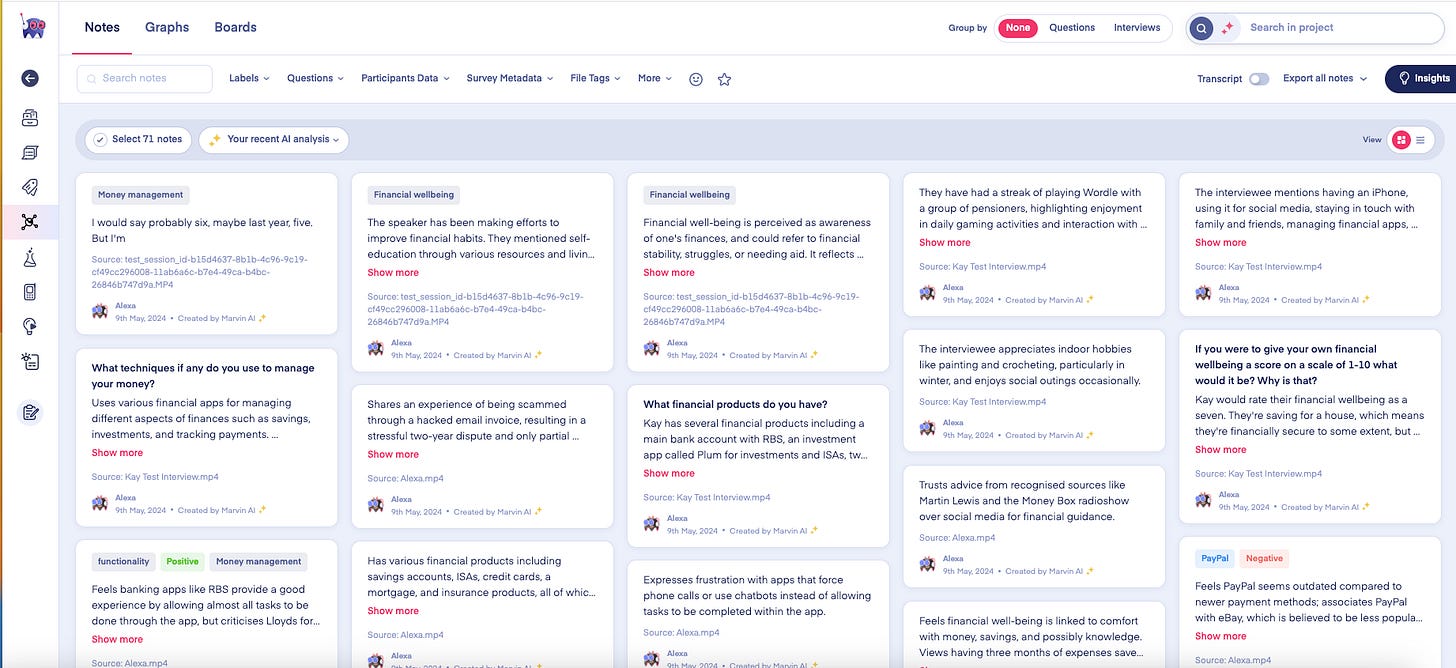
In order to assess the products on a level playing field, I decided to create a mock data set. I enlisted some of my fellow Nilers to create a series of research interview videos, based loosely on a challenge being faced by a real client.
My investigation focused on tools that would assist me with the qualitative workflow. I looked at where these tools could help me right across the research process – from planning to reporting. My biggest interest was at the analysis phase, as that’s where everyone says it will have the biggest impact.
Where I was pleasantly surprised
The best tools offered up informative summaries of each individual session and then all the sessions as a whole. I cross-checked theirs with my own, and was happy with the accuracy. They also:
Allowed me to interrogate the research sessions, asking queries of the data relevant to my objectives.
Let me code and organise my data, but also offered AI support at each stage as an option, letting me speed up and cross-check as I went.
Offered up reference points for each statement claimed in the summaries and themes, which let me track back to each relevant point in the transcripts.
Went beyond the information obtained in the videos, and brought in relevant societal and contextual information, which felt closest to AI giving me real insight.
Where I was disappointed
However, it wasn’t all rosy. Some of the tools I evaluated also had some significant deficiencies.
One offered up summaries that suggested one type of behaviour when in fact it was another, impacting how we would interpret motivations. For example, the AI suggested that our participants preferred to use debit cards online and Apple wallet in store; however, in our mock data set, while three people did mention using debit cards online, they all stated they preferred the convenience of Apple or Google Pay in the most situations on or offline.
In addition, some of the worse-performing tools:
Didn’t cite sources from the videos in their summaries.
Didn’t support data organisation or insight creation.
Provided summaries that were either written conclusively (with errors), or were so vague they lacked value.
Suggested several participants said something when it was just one, giving undue prominence to a particular behaviour or observation.
Stand-out AI-assisted tools
I won’t name and shame, but I will name the tools that I found did a great job. From my evaluation, the stand-out tool is one called Marvin. This isn’t an endorsement – in fact, I’m still playing around with it. But having tried its survey analysis capabilities too, so far it’s looking good. My open-ended analysis has been streamlined significantly with clear citations and evidence provided.
There are also some great tools available for usability and evaluative-type research, such as Maze, which can be used for AI-assisted capture and analysis of behavioural data.
There have also been some big steps forward in AI-supported survey tools, usually with AI embedded to help with suggesting questions and removing biases and closed or leading questions. Some of the more advanced survey packages even support live/dynamic follow-up questions, based on respondents’ earlier answers. Among these, I’m excited about Listen Labs, which I’m exploring to achieve a more conversational, almost qualitative experience with surveys.
Finally, an area where AI is purported to help researchers is sentiment analysis; however, AI doesn’t always pick up on the nuances of the English language. Through manual spot-checking, I found multiple inaccuracies across several different sentiment analysis tools – these still have some way to go.
Where do we go from here?
I’m a champion of ethical design research. The way I approach my general practice also applies to using AI in Research. While experimenting with these new AI tools, some principles jumped out:
Continue to prioritise data privacy. As with any ethical research, we have to ensure that we protect participants’ data, and that the data is collected with informed consent. Luckily, some tools (like Marvin) scan videos to de-identify particular sections, pieces of data and people’s faces. These tools give me the confidence that they are taking privacy as seriously as a researcher should.
Be transparent. It’s essential that we communicate how AI is being used in the research process, data collection and analysis. Include it in your consent forms and client agreements.
Always cross-check the validity of the AI’s output. Has it been able to summarise accurately? Run mock trials to test it out on ‘safe’ data. Ask what data it’s trained on. Look for any gaps in what it’s presenting back. It’s not a panacea for all research challenges and the tricky stuff – it’s actually best at helping with the easy (time consuming) bits.
Collaborate. As researchers, as designers, as product developers, we need to talk and share as we go. It’s essential that we learn from each other's successes and failures. We need to work with rules and policies as they emerge, but the ways that we do that might vary and lead to different successes.
Continue to be mindful of bias. We need to work collectively on this, to talk about and actively to reduce bias in AI by using inclusive and diverse data, algorithms and training datasets. Don’t be afraid to ask difficult questions of the tools and platforms you’re using.
Reflections on AI for researchers
I am just at the beginning of my exploration with AI and what it can do for researchers, but I’m cautiously optimistic, with a dash of scepticism to keep me grounded.
For me AI is currently best-placed as a thinking partner, something you can test out your first-pass ideas with, use as a jumping-off board, or to cast a critical eye over your thinking with a set of known rules. It’s also helpful for taking care of some of the more mundane tasks, but struggles to generate meaningful insights (if any sort of insight).
AI has a place in analysis, but it will not do it for you, yet. The pace of change is, of course, relentless, with some predicting a future GPT-5 might be working at the level of a postgraduate or even PhD.
Right now, even the makers of the apps themselves will tell you not to rely solely on AI for research. This is a time for cautious exploration, but always backed by an intimate knowledge of your data set, and double-checking the outputs. The human factor is – for the time being – essential.
So, for now, I’m reassured that this very human Alexa is here to stay.
For now.
Nile News
FCA Tech Sprint
Our Principal Consultant, Jonty Fairless, headed to Glasgow this month to see some of the really innovative ideas emerging from the FCA's Financial Inclusion TechSprint.
The idea behind the TechSprint is to support the creation and development of technology-driven projects that will increase financial inclusion.
The three areas chosen as the particular focus were:
Increasing the likelihood of consumers being accepted when applying for everyday financial services, like ordinary bank accounts, credit cards and insurance.
Improving outcomes for consumers who get declined when applying for a product, or excluded when a product changes and is no longer suitable for their needs.
Deploying technology to create better outcomes for groups who have traditionally been poorly-served by retail banking, payments, credit and insurance.
You can watch Jonty’s report from the event over on our LinkedIn page.
AI in the here and now
What tangible benefits is AI actually bringing to businesses today?
That was the question at the heart of our latest Changemakers' Breakfast in Edinburgh, which brought together a diverse group of senior leaders working in different sectors and roles from across our clients.
Across the group, confidence levels in AI initiatives varied, but were not yet high. Many organisations are still cautiously exploring this new technology, while for some it’s simply not yet a priority – they’re planning to invest when things have developed a little further.
The group felt that smaller organisations might have the edge when it comes to realising high-value results quickly with AI. Larger organisations, however, should anticipate a longer ROI period, potentially 3-5 years, and build this into their strategy.
Many of those around the table said their businesses are already exploring Microsoft CoPilot, initially taking advantage of features like meeting transcripts, capturing tacit knowledge, and improving findability of information across the business.
Overall, the mood is still one of cautious experimentation. Our conversation highlighted the breadth of opportunity to tap into AI, but also the need to ready the organisation – both in terms of practical matters like data hygiene, and also strategically and culturally – before jumping into the technology implementation itself.
Inspire Launch Grow
We were pleased to attend the University of Edinburgh’s Inspire Launch Grow event on 6th June, celebrating upcoming entrepreneurs.
It was great to see the investment community coming together to champion up-and-coming businesses — they are building a great ecosystem to support entrepreneurs in the city, and the Nile team love supporting and coaching these future entrepreneurs.
If you find The Navigator valuable, please spread the word by sharing it with your friends and colleagues:
About Nile
We’re a strategic design company that delivers human-centred change in highly regulated industries. Here’s three ways we can help:
Strategic projects - We’ll help you de-risk outcomes, saving time and money without compromising experience.
Accessibility - We can help you get accessibility right, as a fundamental part of inclusion.
Talent - Supercharge your internal change efforts with our Trusted Talent service – long-term placements of expert people who’ll help you deliver key transformation and BAU outcomes.
If you’d like to know more, just reply directly to this email (they come straight to my inbox), or reach out to someone specific via our website.
Thanks for reading! 🚀